
Compared with cables, optical fibers have many advantages as transmission media. However, quartz fiber for common communication is difficult to connect, expensive, and expensive to install and maintain, and cannot be widely used for short-distance data communication or desktop data connection. Plastic optical fiber not only has the advantages of optical fiber but also has a diameter of generally 0.3 to 3 mm. The large diameter is suitable for connection, and the coupling efficiency of light is also high. At the same time, it is also soft, bending resistant, shock resistant, radiation resistant, and inexpensive. Convenient construction and other advantages can replace the traditional quartz fiber and copper cable to a certain extent. Therefore, the plastic optical fiber communication system is very suitable for short-distance (100m or so), medium and small capacity (several Kb/s to 100Mb/s), low-cost (tens of dollars) desktop data connection, and data between devices and device internal bus. connection.
Advantages of plastic optical fiber transmission systems After replacing cable connections with plastic optical fiber communication systems, the performance of the equipment will be improved in the following aspects.
● Improve the equipment’s ability to resist electromagnetic interference and nuclear radiation.
● No crosstalk. Optical cables are used to transmit signals without crosstalk between the signals.
● Lighten the weight of the system. The weight of a 1500m diameter 1mm plastic fiber is less than 2kg.
● Strong anti-lightning ability. The metal-free cable itself is a good insulator, and even if it is exposed to the outside, it will not cause lightning to damage the equipment.
System Description of Plastic Optical Fiber Communication The basic components of a plastic optical fiber communication system is: optical transmitters, optical receivers, plastic optical fibers, and some passive components. An optical transmitter converts an electrical signal (such as a TTL level signal) into an optical signal that is coupled into a plastic optical fiber and transmitted through a plastic optical fiber to an optical receiver that reduces the optical signal to an electrical signal (eg, TTL) Level signal).
The plastic optical fiber communication system focuses on short-distance communication, low cost, simple operation, and high reliability, so it is completely different from the quartz optical fiber communication system in the realization of the specific system.
Plastic optical fiber communication transceiver
The plastic optical fiber transceiver is the core part of the plastic optical fiber communication system, including the optical transmitter and the optical receiver.
1 is a schematic diagram of the structure of an optical transmitter. The light-emitting diode (LED) is a high-brightness surface mount light-emitting diode for common display and has a driving current of less than 20 mA and a center wavelength of 590 nm (orange light). The reason why the 590nm LED is chosen is because the LED of this wavelength is very cheap, and the loss value of the plastic fiber is relatively low at the wavelength of 590 nm. The size of the LED chip is about 1.0mm×1.0mm, which is equivalent to the diameter of the plastic fiber, and it is easy to couple the optical signal into the plastic fiber.
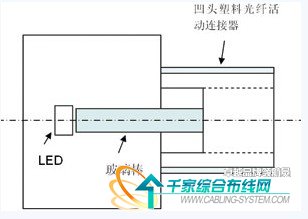
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the structure of an optical transmitter
The external input TTL level signal is FSK frequency modulated, and the TTL level signal is converted into a carrier signal more suitable for plastic optical fiber transmission to drive the LED illumination. The light signal from the light-emitting diode (LED) is directly coupled into a glass rod of 1.0 mm diameter, which is then coupled into a plastic optical fiber having a diameter of 1.0 mm through a glass rod.
2 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the optical receiver. The photodetector detects the optical signal and generates an induced current, and then is amplified by the amplification module in two stages, and is input to the FSK demodulation module to be demodulated by the flip-flop. The demodulated signal still contains high-frequency interference, which is filtered by the filter module and then judged by the decision module to be restored to the input TTL signal.
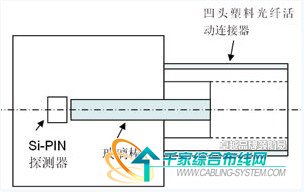
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the optical receiver structure
Both of these plastic fiber optic transceiver solutions are targeted for point-to-point connections. The transceiver of the bus type plastic optical fiber communication system should be a bus type. In the photoelectric conversion, the bus type plastic optical fiber communication transceiver and the point-to-point type plastic optical fiber communication transceiver are the same, but the bus type plastic optical fiber communication transceiver is half duplex. In the mode of operation, it has only one optical signal input/output port, or it has only one concave plastic optical fiber movable connector. At this time, the glass rod of the concave plastic optical fiber movable connector is connected with the LED and the Si-PIN. The end face is not a vertical way, but a 45° bevel, so that the beam can be split into two, one way to Si-PIN, all the way to the LED. Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of a bus type of plastic optical fiber communication transceiver.
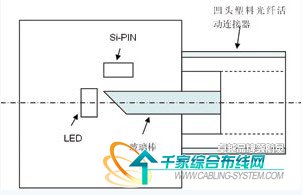
Figure 3 bus type plastic optical fiber communication transceiver
Plastic fiber optic patch cord
Plastic fiber optic patch cords are used to connect plastic fiber optic transceivers to plastic fiber optics by coupling optical signals into plastic fibers. Similar to cable connectors, it is divided into two types: concave head and convex head. The recessed plastic optical fiber active connector and the plastic optical fiber communication transceiver are integrated, and the male plastic optical fiber connector is connected to the plastic optical fiber.
The mechanical structure of the plastic optical fiber movable connector can be variously selected. Because the diameter of the plastic optical fiber core is large, the plastic optical fiber movable connector and the currently used quartz optical fiber movable connector can be completely different, and can follow the structure of the current cable connector ( Such as SMA structure), not only the connection loss is small, but also the use of wire clamps and electrician blades, it is convenient to complete the assembly of plastic optical fiber movable connector parts in the field.
Plastic optical fiber fixed connector
Plastic fiber optic fixed connectors are used for the connection of plastic and plastic fibers. Using a V-groove structure, two plastic optical fibers are placed in a V-shaped groove, and the plastic optical fiber is fixed by a metal material, and then a heat-shrinkable sleeve is packaged to complete the fabrication of a plastic optical fiber fixed connector. The V-groove structure can achieve the purpose of quickly and easily making a plastic optical fiber fixed connector, and the connection loss is not large due to the large diameter (1 mm) of the plastic optical fiber.
Plastic optical bus branch
Plastic fiber optic bus splitters are used in bus-type plastic fiber optic communication systems. As shown in Fig. 4, the optical input signal of any one port is evenly distributed to other ports after being totally reflected by the glass rod and reflected by the end face of the glass rod. The requirement for the plastic optical fiber bus splitter is that the additional loss is low, the second is that the uniformity of each port is good, and the third is that the structure is simple and the cost is low.
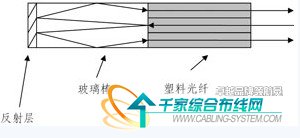
Figure 4 plastic optical fiber bus splitter
Plastic fiber optic light multimeter
The plastic optical fiber multimeter consists of a light source, an optical power meter, a microprocessor, and a liquid crystal display. The LED is used as the light source and the Si-PIN is used as the detector. It is similar to the fiber optic multimeter currently in use, except that the wavelength range of light used is different and the cost is different.
Key Technology Low-Cost Plastic Optical Fiber Communication Transceivers Plastic optical fiber communication transceivers should be high-sensitivity, bursty receivers and extremely low-cost fiber optic transceivers. The principle of the plastic optical fiber communication transceiver is relatively simple, but requires the circuit cost to be extremely low, and also ensures high receiving sensitivity, high reliability, and small size. At present, the system has realized the transmission sensitivity of the transmitting end -10dBm, and the receiving sensitivity of the receiving end is -40dBm (10E-9 error rate).
Plastic fiber optic patch cord
The key technology of the plastic fiber optic patch cord is that it is simple to manufacture and low in cost. It can be easily assembled on site by using simple tools such as wire clamps and electrician blades. Its connection loss is less than 1dB.
Plastic Optical Fiber Bus Splitter The plastic optical fiber bus splitter is a key component for implementing a bus-type plastic optical fiber communication system. The optical input signal of any one port is evenly distributed to other ports.
It seems to be the 1×N optical splitter that is commonly used nowadays. In fact, the principle and function are different. A 1×N optical splitter distributes the optical input signal of one port evenly to other ports or concentrates the optical input signals of N ports onto one port, and the plastic optical fiber bus splitter requires any port. The optical input signal is evenly distributed to other ports. It is a half-duplex device. In the normal operation of the bus-type plastic optical fiber communication system, only one port has an optical signal output, and the remaining ports are input optical signals. It is used in conjunction with a bus-type plastic optical transceiver to form a bus-type plastic optical fiber communication system. It not only requires a simple structure but also requires a low cost.
Original Article Source http://cabling.qianjia.com/html/2009-09/09_192636.html