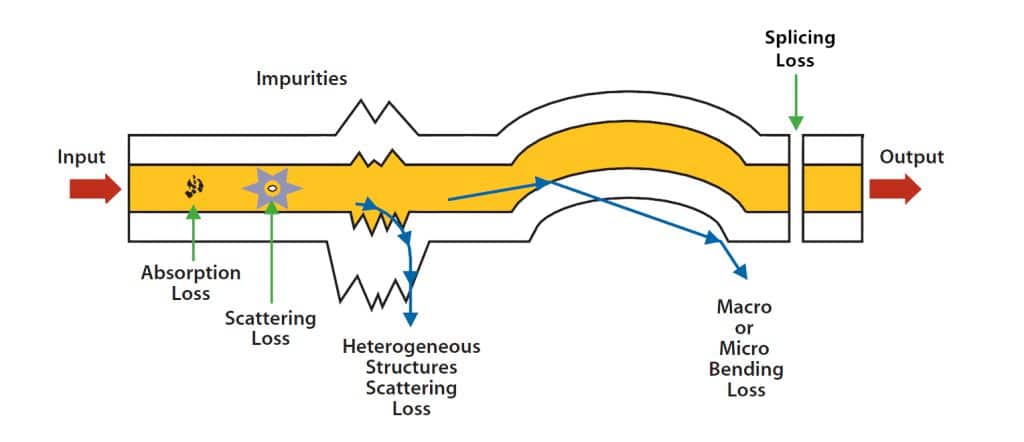
The principle of loss in fiber optic wiring
The fiber optic wiring must be such that the core portion through which the light passes is positioned correctly.
The wiring loss of the optical fiber is mainly caused by the following reasons.
(1) Axis offset
The optical axis offset between the connected fibers can cause wiring loss. In the case of a generalized single mode fiber, the wiring loss is approximately the square of the axis offset multiplied by a value of 0.2. (For example, when the wavelength of the light source is 1310 nm, the wiring loss is about 0.2 dB when the axis shift is 1 μm)

(2) Angle shift
The angular offset between the optical axes connecting the fibers can cause wiring losses. For example, if the angle of the section cut by the fiber cutter before the fusion becomes large, the fiber is wired in an inclined state, so care must be taken.

(3) gap
The gap between the end faces of the fibers causes wiring loss. For example, if the end faces of the fibers that are mechanically spliced are not properly bonded, they can cause wiring loss.

(4) Reflection
When there is a gap in the end face of the fiber, due to the difference in refractive index between the fiber and the air, the wiring loss is caused by the reflection of a maximum of 0.6 dB. Also, in order to prevent light breakage, it is important to clean the fiber end face on the optical connector. However, there is a loss of rubbing on the end face of the optical connector other than the end face of the optical fiber. Therefore, it is important to clean all the end faces of the optical connector.
Disclaimer: All information indicated as other sources is transferred from other platforms, the purpose is to convey more information, does not represent the views and positions of this site. Please contact us if there is any infringement or objection.